Handbook Of Solid Phase Microextraction Pdf

Mar 16, 2011. Historical Perspective and Development of Fiber Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME). Theory of SPME. Rational Design of SPME Devices. On-Site Samplers. Hyphenation of SPME and GC. Hyphenation of SPME and LC. Concluding Remarks. Get PDF: This Chapter (369K)All Chapters. Germanium is a chemical element with symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its.
The relatively new technique of solid phase microextraction (SPME) is an important tool to prepare samples both in the lab and on-site. SPME is a 'green' technology because it eliminates organic solvents from analytical laboratory and can be used in environmental, food and fragrance, and forensic and drug analysis. This handbook offers a thorough background of the theory and practical implementation of SPME. SPME protocols are presented outlining each stage of the method and providing useful tips and potential pitfalls. In addition, devices and fiber coatings, automated SPME systems, SPME method development, and In Vivo applications are discussed. This handbook is essential for its discussion of the latest SPME developments as well as its in depth information on the history, theory, and practical application of the method.
Key Features. Dedication Preface List of Contributors 1. Solid-Phase Microextraction in Perspective 1.1.
Sample Preparation as Part of the Analytical Process 1.2. Classification of Extraction Techniques 1.3. Perspective on Microextraction Techniques 1.4. Implementations of SPME 1.5.
Miniaturisation and Integration 1.6. In Vivo Analysis 1.7.
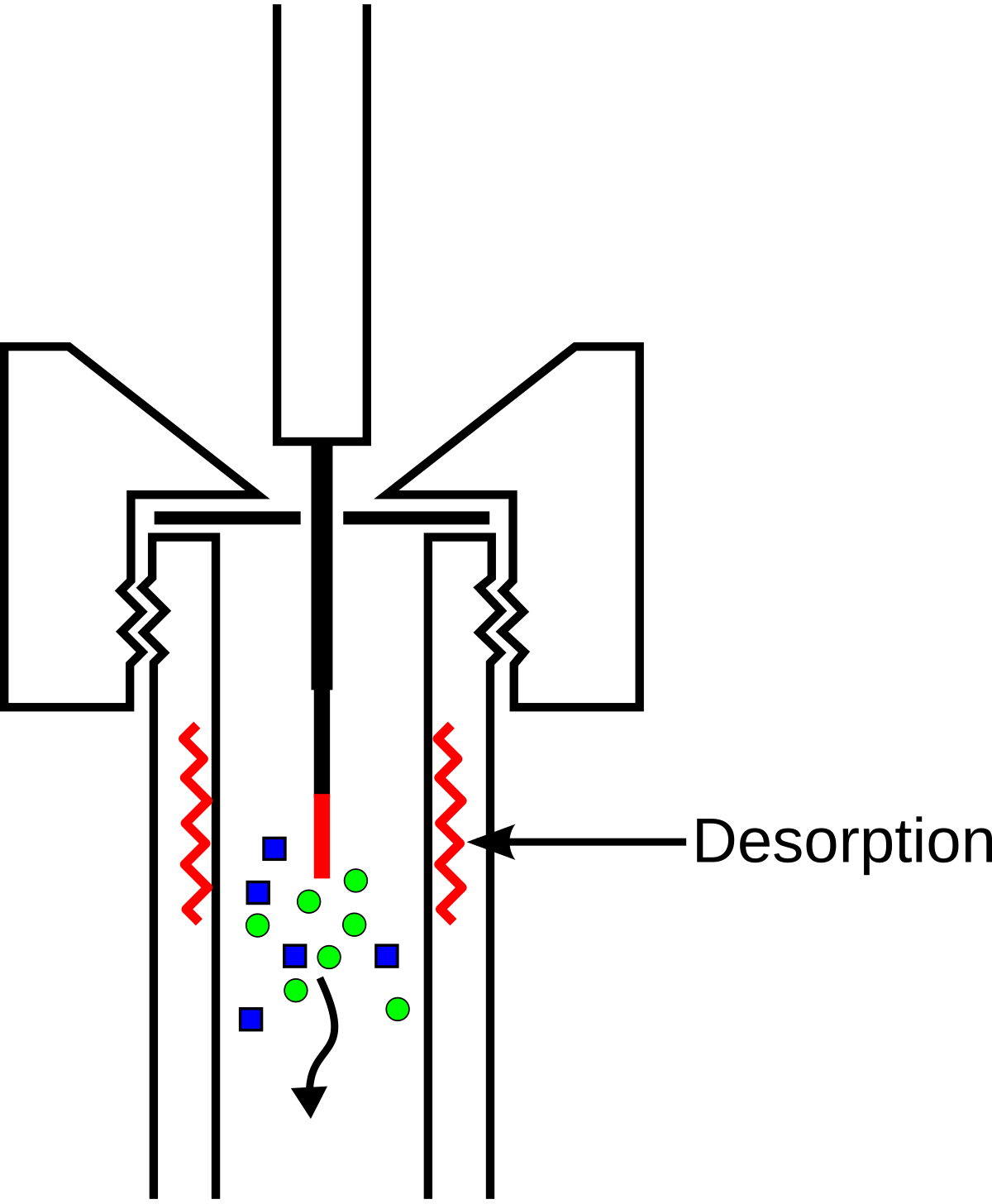
SPME Versus SPE 2. Theory of Solid-Phase Microextraction 2.1. Introduction 2.2. SPME Principle 2.3. Thermodynamics 2.4. Kinetics 2.5.
Extraction with Derivatisation 2.6. Extraction of Sample Matrices Containing Solids 2.7. Solid Versus Liquid Sorbents 2.8. Passive TWA Sampling 2.9. In-Tube SPME 2.10. Experimental Verification 3.
Development of SPME Devices and Coatings 3.1. Historical Perspective 3.2.
Rational Design of SPME Devices 3.3. On-Site Samplers 3.4. Development of New SPME Coatings 3.5. Interfaces to Analytical Instrumentation 4. SPME Commercial Devices and Fibre Coatings 4.1. Introduction 4.2. Description of SPME Fibre Assemblies and Holders 4.3.
Description of Fibre Cores, Coatings and the Coating Process 4.4. A Guide for the Selection of the Appropriate SPME Fibre 5. Automated SPME Systems 5.1.
Automated Solid-Phase Microextraction–Gas Chromatography 5.2. Automated SPME–LC 5.3. Other Automated Configurations Involving SPME 6. Calibration 6.1.
Introduction 6.2. Traditional Calibration Methods for the Quantification of SPME 6.3. Equilibrium Extraction 6.4. Exhaustive Extraction 6. Free Download Graphic Driver For Windows 7 32 Bit. 5. Diffusion-Based Calibration 6.6. Calibration of SPME by Liquid Injection 6.7.
Solid-Phase Microextraction Method Development 7.1. Introduction 7.2. SPME Method Development – General 7.3. SPME Method Development for GC Applications 7.4. SPME Method Development for HPLC Applications 7.5.
Method Validation 7.6. Concluding Remarks 8.
SPME and Environmental Analysis 8.1. Introduction 8.2. Fibre SPME 8.3. In-Tube SPME 8.4.
Applications of SPME in Various Environmental Sample Matrices 8.6. Applications of SPME for Various Analytes in Environmental Samples 8.7. Concluding Remarks 9. Application of Solid-Phase Microextraction in Food and Fragrance Analysis 9. Free Apprenticeship Programs In Dc here. 1. Introduction and Method Development Considerations 9.2. Reviews and Case Studies Involving SPME as an Extraction Procedure 9.3.